R8A Zoning in NYC is a high density residential zoning district. This is contextual zoning which means following the Quality Housing Program requirements. R8A Zoning is found in Manhattan, The Bronx, Brooklyn and Queens.
This post will only be addressing R8A Zoning, here is a list of all the R8 Zoning Districts.
R8 Zoning Districts
Basic R8 District:
R8 Contextual Districts
Commercial Zoning with R8A Residential Equivalent
R8A Zoning NYC
What Is R8A Zoning?
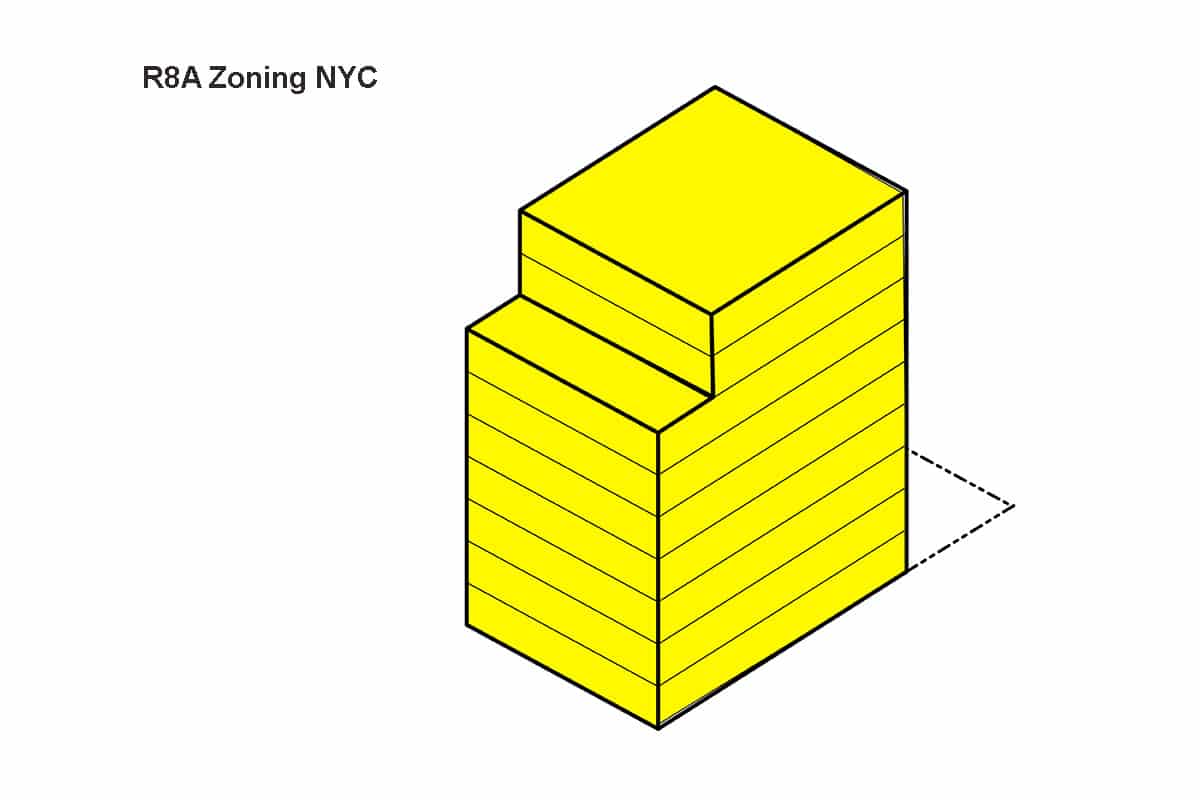
R8A Zoning is considered “high density” residential zoning. It typically has multifamily buildings that are often 9 or 10 stories tall. In an R8A zone you must follow the Quality Housing Program zoning regulations.
Quality Housing Program R8A
The Quality Housing Program is required in R8 Contextual Zoning. Quality Housing promotes shorter wider buildings that are typically larger in square footage then a tall skinny building. The Quality Housing Program is not to be confused with the Inclusionary Housing Program for affordable housing. The Quality Housing Program is a set of optional zoning regulations in certain districts but required for Contextual Zoning. Quality Housing has nothing to do with low income or affordable housing. The Quality Housing Program typically will result in a larger building of a higher quality. There are more zoning floor area deductions in Quality Housing that would give you a boost to your total building size.
R8A Zoning Community Facility
R8A Zoning is a residential zone but Community Facility uses are allowed in all R8 zones. In the instance of a community facility the zoning calculations would typically be different from a residential use. One can also build a mixed use building with both community facility and residential use.
R8A Zoning Commercial Overlay
Sometimes residential districts have commercial overlays. Commercial Overlay Zoning means the zone is primarily residential but commercial use is allowed as an option or you can have both uses as a mixed use building. Here is a link to an article we wrote on Commercial Overlays.
R8A Inclusionary Housing Program
Always check if your property is subject to requirements of the Inclusionary Housing Program. There are areas that have either optional and sometimes mandatory requirements for inducing affordable housing in your development. There can be zoning penalties if you choose not to provide it. And zoning bonuses if you do.
R8A Zoning Regulations For Quality Housing
Lot Size:
Minimum Lot width =18 Feet
Minimum Lot Area = 1,700 Sq Ft
Lot Coverage:
Corner Lot = 100%
Interior or Through Lot = 70%
Floor Area Ratio (FAR):
FAR is Floor Area Ratio which determines the maximum square footage of the building.
FAR = 6.02
With Inclusionary Housing Bonus FAR = 7.20
Density Factor
680
Building Base Height: This indicates a setback is required at these heights
Base Height = 60 Minimum / 85 Maximum (95 for Qualifying Ground Floor)
A setback is required in the base height range. Or this can be the maximum height of the building without a setback.
Inclusionary Housing Base height
Base Height = 60 Minimum / 105 Maximum
A setback is required in the base height range. Or this can be the maximum height of the building without a setback.
Overall Building Height: This is the maximum building height
Max Building Height = 120 feet or 125 with Qualifying Ground Floor
Inclusionary Housing Building Height
Max Building Height = 140 feet or 145 with Qualifying Ground Floor
Always check if your building is subject to Sliver Law zoning restrictions for properties or buildings less than 45 feet wide. The sliver law is an additional restriction on the height of the building and supersedes the typical building height requirements.
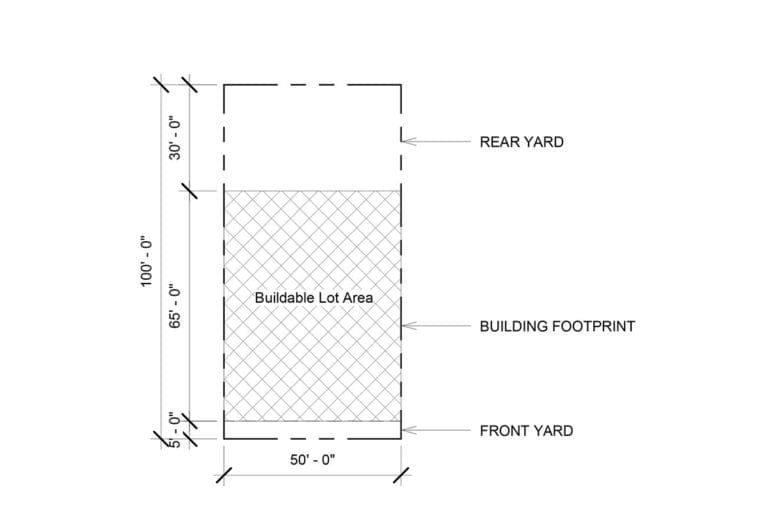
Yards:
Corner Lot: No Yards Required
Interior Lot = 30 foot minimum rear yard required
R8A Zoning Example
Here is an example analysis. Be aware that zoning is complicated and I am only addressing the basics here. I assure you there are many additional issues and variations to consider beyond this example.
R8A Zoning Example Lot
Lets assume we have a 50 foot wide and 100 foot deep property in an R8A Zoning District in Manhattan in Harlem on an interior lot. Check out another post to learn about the different lot types.
Zoning Floor Area/ Floor Area Ratio (FAR)
The floor area ratio is 6. 02. The FAR is a ratio that determines how many square feet you can build on the property. You take the property size and multiply it by the FAR.
In this example we have:
FAR of 6.02
Lot Size of 50 feet x 100 feet.
Zoning Floor Area = Lot Area X FAR
Lot Area = 50 x 100
Lot Area = 5,000 sq ft
FAR = 6.02
Zoning Floor Area = 5,000 sq ft x 6.02
Zoning Floor Area = 30,100 sq ft
R8A Zoning Example Conclusion
In this example we are proposing to build a 30,100 sq ft building. The apartment building will be 9 stories tall and have a setback at least on the top floor. The Building will have a foot print of 50 x 70. It will have a maximum of 44 apartments but can have less as well.
NYC Zoning Codes R8A
As an architect I study zoning very closely. NYC Zoning is complicated and quite involved. In this article we reviewed some of the basic Zoning Codes with regards to commercial zoning district R8A. This analysis does not assume to cover every possible issue and condition, but provide a general overview. This blog post does not substitute understanding the NYC Zoning Resolution.
Thank You for reading our Blog Post on R8A Zoning
I hope this was helpful. If you want to discuss a specific project with an architect please feel free to Contact Fontan Architecture. We will be happy to help.
Request a Consultation with Fontan Architecture

This post was written by Jorge Fontan AIA a Registered Architect and owner of New York City architecture firm Fontan Architecture. Jorge Fontan has earned 3 degrees in the study of architecture including two degrees from the City University of New York and a Masters Degree in Advanced Architectural Design from Columbia University. Jorge has a background in construction and has been practicing architecture for 20 years where he has designed renovations and new developments of various building types.